this week's goals
- finish associate data scientist in python track on datacamp
- finish frontend development libraries track
'TIL FINAL YEAR OF UNI
today's checklist
- complete datacamp course 29: hypothesis testing in python
- ✔ complete freecodecamp project: build a random quote machine
- ✔ maru hiragana
tags
backend
frontend
languages
freecodecamp project: building a random quote machine
finished at 13.13
for this project i used jquery since i'm not confident in react yet, plus i still find it slightly confusing
these were the requirements of the project
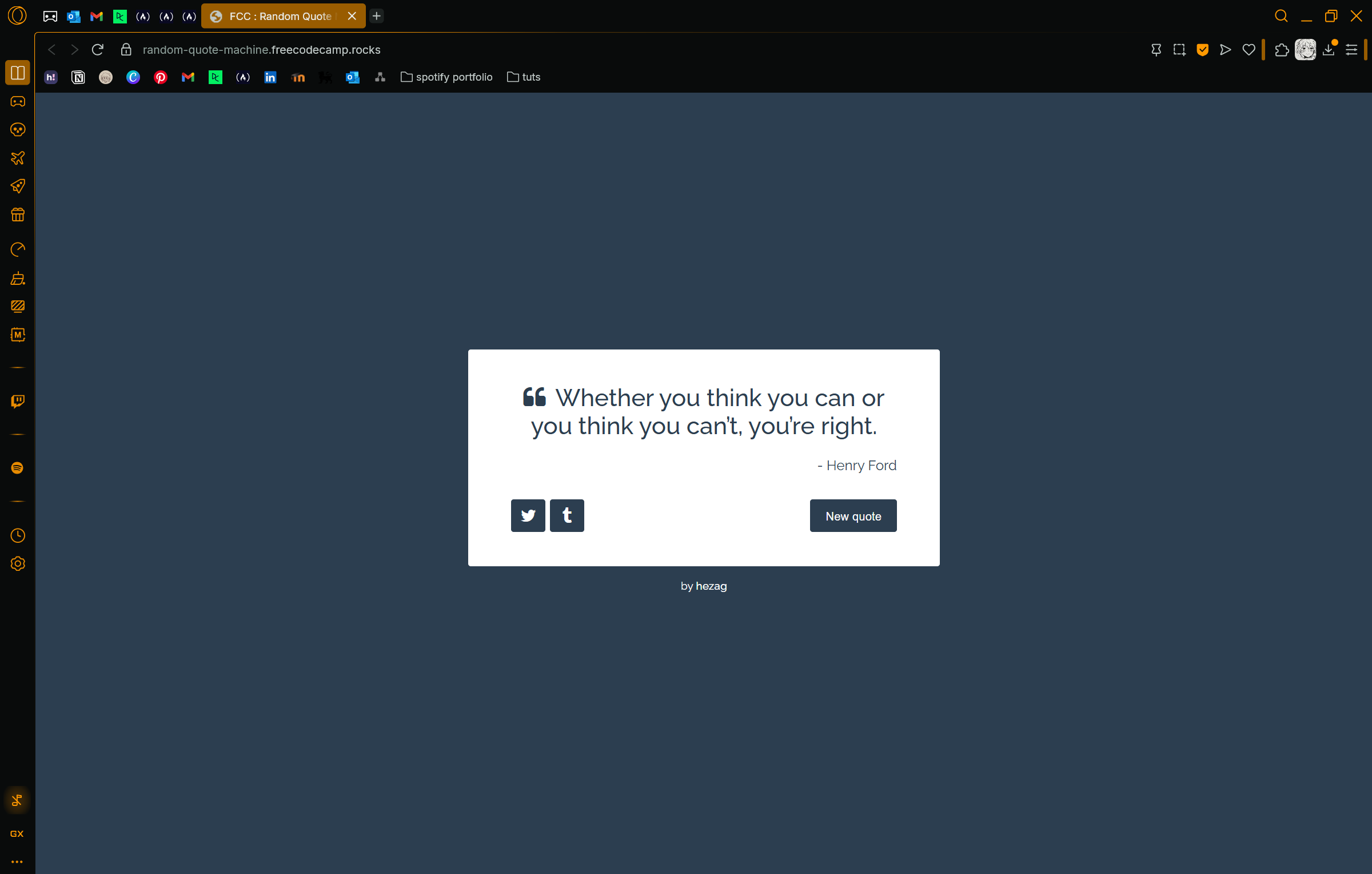
and this was the example of a completed project
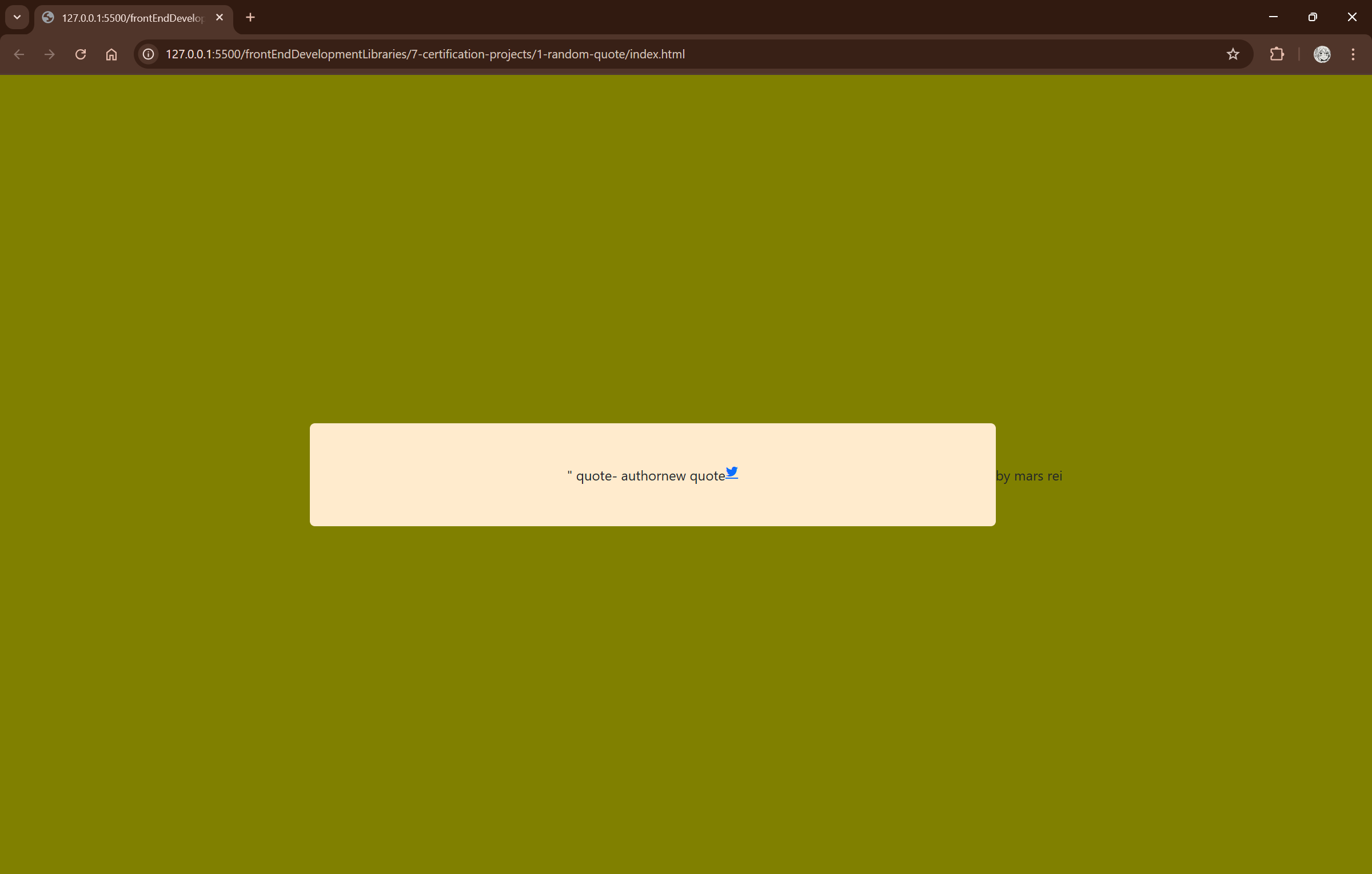
this was without major styling
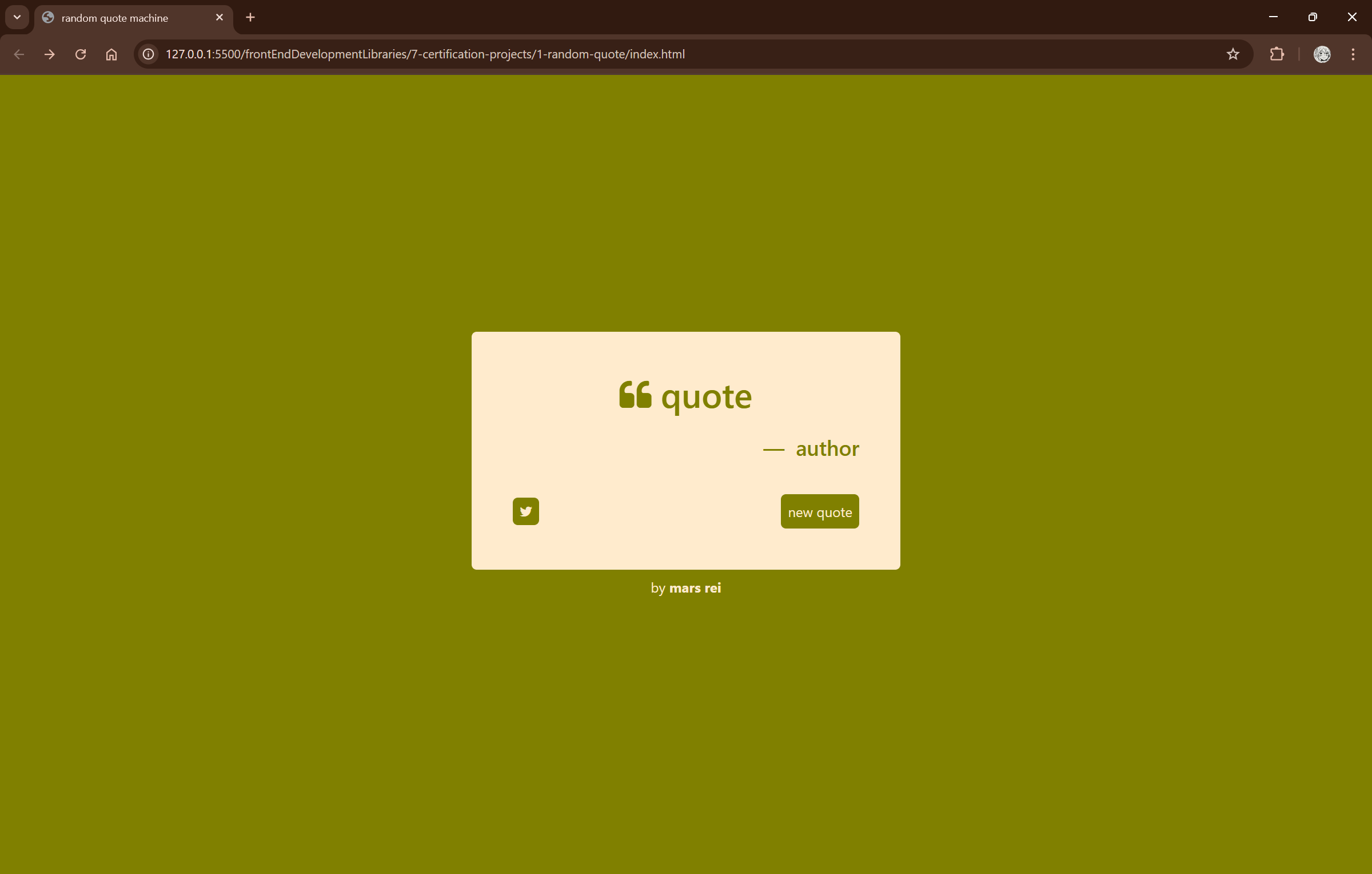
and this was the final styling
for my random quote generator, i’ll use the anime chan api to generate random anime quotes (most of the api’s i wanted to use are limited / not up)
in the end, the quotes didn’t end up generating, my code passed all the tests


at the end of the day i ended up making a project using this - a random lyric generator!
datacamp course: hypothesis testing in python
started at 16.36 and finished at 19.46
i’m probably gonna do half a datacamp course per day from today onwards as it can be a lot of information to digest (as you will see below in the form of some worded notes)
chapter 1: hypothesis testing fundamentals
-
hypothesis tests and z-scores
- we use hypothesis testing to determine whether sample statistics are close to or far away from expected (or ‘hypothesised’ values)
- standard normal (z) distribution: normal distribution with mean = 0 + standard deviation = 1
-
p-values
- hypothesis - a statement about an unknown population parameter
- hypothesis test - a test of 2 competing hypotheses
- null hypothesis (H0) is existing idea (initially assumed to be true)
- alternative hypothesis (HA) is the new ‘challenger’ idea of researcher
- test ends in reject H0 or fail to reject H0
- if evidence from sample is ‘significant’ that HA is true, reject H0, else choose H0
- significance level - ‘beyond a reasonable doubt’ for hypothesis testing
- hypothesis tests check if the sample statistics lie in the tails of the null distribution
- two-tailed tests if the alternative hypothesis is different from the null hypothesis
- right-tailed test if the alternative hypothesis is greater than null
- left-tailed test if the alternative hypothesis is less than null
- p-value - probability of obtaining result assuming null hypothesis is true
-
statistical significance
- p-values quantify evidence for null hypothesis
- large p-value → fail to reject null hypothesis
- small p-value → reject null hypothesis
- significance level of a hypothesis test (gamma) - threshold point for ‘beyond a reasonable doubt’
- common values of a significance level: 0.2, 0.1, 0.05, 0.01
- if p ≤ gamma, reject H0, else fail to reject H0
chapter 2: two-sample and anova tests
-
calculating p-values from t-statistics
- t statistic follows t-distribution, has a paremeter called ‘df’ / ‘degrees of freedom’, and looks like normal distritbutions but with fatter tails
- the larger the degrees of freedom, the closer the t-distribution gets to the normal distribution
- normal distribution is the t-distribution but with infinite df
- degrees of freedom - max num of logically independent values in the data sample